Rationale and research:
This week in CEP 811 our assignment was to create a lesson that could be implemented into our current classroom. The lesson connected our maker kit (Makey Makey), found items, and research on learning, content knowledge and pedagogy (TPACK). My research last week focused on collaborative learning and the benefits when positive interaction is displayed in times of uncertainty. Michelle Jordan and Reuben McDaniel Jr. found, “that when uncertainty is experienced and expressed in conjunction with peer support, then uncertainty generates a platform for learning” (Jordan & McDaniel, 2014). Peer interaction is influential because students rely on supportive social responses to enact most of their uncertainty management strategies. My lesson plan is in the content areas of Math and Music. Through scaffolding, students can combine their understanding of the topic to have collaborative success (O’Donnell, 2012).
Along with peer collaboration I also wanted to incorporate immediate feedback into this lesson in the form of Makey Makey and setting up the DJ Booth correctly with the circuits. If alligator clips and circuits are set up incorrectly the program will not work, resulting in immediate feedback. Students then will have to brainstorm and refine their prototype. Emily R. Fyfe and Bethany Rittle-Johnson conducted research using 88 second grade students to study the benefits of feedback. Their journal The benefits of computer generated feedback for mathematics problem solving including data that implicated immediate feedback improves learning experiences (Fyfe & Johnson, 2015 p. 240). Some researchers believe that feedback should be given immediately after a response in order to eliminate incorrect ways of thinking and reinforce correct ones (Skinner,1954). According to Fyfe and Johnson, immediate feedback may provide motivation to practice.
Lesson Plan:
DJ Pattern
2nd Grade Math/Music Lesson Plan
Standards:
ISTE
- Innovative Designer: Students use a variety of technologies within a design process to identify and solve problems by creating new, useful or imaginative solutions. (A) Students know and use a deliberate design process for generating ideas, testing theories, creating innovative artifacts or solving authentic problems. (C) Students develop, test and refine prototypes as part of a cyclical design process.
- Global Collaborator: Students use digital tools to broaden their perspectives and enrich their learning by collaborating with others and working effectively in teams locally and globally. (C) Students contribute constructively to project teams, assuming various roles and responsibilities to work effectively toward a common goal.
Student Learning Objectives:
- Students will be able to create a personalized sound using Scratch and Makey Makey.
- Students will learn and explore patterns in music giving them an opportunity to practice making repeated patterns.
- Students will work positively in collaborative groups and respond positively in times of uncertainty.
- Students will be able to create repeated patterns using the Makey Makey kit and the Scratch program. (https://scratch.mit.edu/projects/169900902/)
Materials:
- Makey Makey Kit
- Alligator clips
- Empty cereal boxes (DJ booth)
- Laptops
- Scissors
- Play-Doh
- Whiteboards
- Dry erase markers
- Paper and pencils (exit slip)
Day1 procedure (approximately 45 minutes):
- Students each have a small whiteboard, dry erase marker and sock (eraser) at their seat.
- Teacher will show the students a ABCDE pattern and have students predict what letter will come next.
- Write it down on whiteboards and show when directed.
- Show a EDCBA and have students write on whiteboards the pattern two more times.
- Have students turn and talk to their table partner and share.
- Have a student or group share their thoughts.
- Teacher listens for possible misconceptions and clarifies any misconceptions.
- Teacher allows students to collaborate with the students at their table for different examples of repeated patterns using the letters A, B, C, D, E.
- Teacher allows students time to share out some repeated patterns.
- Students should select groups of 3-4 (or teacher can select for them) to get started on the Maker lesson.
- Group Work: Everyone participates, everyone shows respect, everyone is focused on the task, one person speaks at a time, be nice – compliment each other!
- Each group will have a small tub of Play-Doh and a shoe box.
- Groups may spend the next 30 minutes designing their DJ Booth, each booth must have 5 buttons made out of Play-Doh (A,B,C,D,E). Students must write a letter next to each corresponding Play-Doh button.
Day 2 procedure (approximately 45 minutes):
- Reminder: Positive group work guidelines: Everyone participates, everyone shows respect, everyone is focused on the task, one person speaks at a time, be nice – compliment each other!
- Groups should login to Scratch and go to the Makey Makey DJ on Scratch (https://scratch.mit.edu/projects/169900902/)

- If students want to keep the programmed sounds as they are they then can move onto step 5 for today (connecting the alligator clips to the correct letters on their DJ booth).
- If students choose to re-mix their sounds they can by clicking on the “see inside” button on the screen. Groups then can choose the sound for each corresponding Play-Doh letter button.
- Students are then to connect one end of the alligator clip into the Play-Doh and the other end into the Makey Makey board. Please make sure each Play-Doh button is set up correctly. Up arrow = A, right arrow = B, down arrow = C, and left arrow = D, spacebar = E.
- One clip needs to be connected to the Earth and you will need to hold onto this clip when selecting a letter.
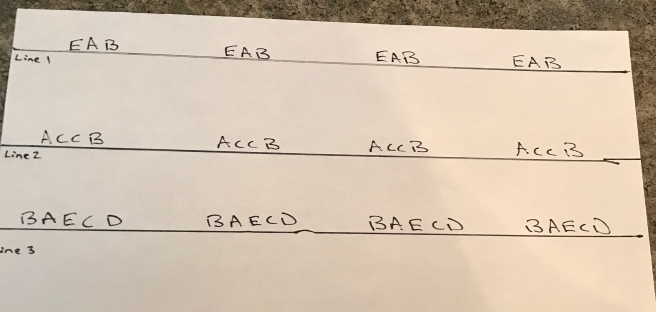
- As a group students should play around with the sounds and put them in an (ABC) pattern on line one. (i.e. ABC, or BAC, or EAB). This pattern should be repeated 4 times. Test your sound for line one, if group agrees and likes the sound write the pattern down on line one and then move onto line two.
- As a group students come up with an (ABCD) pattern for line two. (i.e. BACD, or ABCD, or EDBA). Test your sound for line two, if group agrees and likes the sound write the pattern down on line 2 and then move onto line three.
- As a group students come up with an (ABCDE) pattern for line two. (i.e. BDBA, or ADBC, or EDBAD). Test your sound for line three, if group agrees and likes the sound write the pattern down on line three. Test out all three lines and your completed sound.
- Revise and edit if needed.
- Extension/Time available: Groups may perform one pattern line and have the class guess what the pattern is.
Assessment:
I will be able to assess the students’ learning by circling the classroom, listening to conversations, checking in with groups and listening to their discussions as well as exit slips provided at the end of the lesson.The overall goal of the lesson is for students to understand patterns by remixing a Scratch program using their Makey Makey and their own creativity. Students are given the requirements and the materials for the game, however they are assessed on their ability to make it their own. Exit slips: Have children draw two different ABCDE patterns and answer questions below about their Making process and collaborative groups:
- What was helpful about having group members for this task?
- Was it easier to work with other students? Why or why not?
- How did you break up the work amongst your team members? Why?
- What was challenging about working with Makey Makey and Scratch?
References
Culatta, R. (2013). Reimagining learning [Video]. Retrieved from https://ed.ted.com/on/5TOxVl1F
Fyfe, E., Rittle-Johnson, B., (2016) The benefits of computer generated feedback for mathematics problem solving. Department of Psychology and Human Development https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301223661_The_benefits_of_computer-generated_feedback_for_mathematics_problem_solving
Jordan, Michelle. McDaniel, Reuben. “Managing Uncertainty During Collaborative Problem Solving in Elementary School Teams: The Role of Peer Influence in Robotics Engineering Activity.” Journal of the Learning Sciences, 2014 (490-536). Taylor & Francis Online. Web. 19 July 2017.
Skinner, B. The science of learning and the art of teaching Harvard Educational Review, 24 (1954), pp. 86–97
Snyder, M. (2017). DJ Pattern with Makey Makey and Scratch. [Video]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qdj7m9fgZbY


